Abstract
Background: The interleukin (IL)-3 receptor α-chain, CD123, is the primary low-affinity subunit of the IL-3 receptor. CD123 is expressed at various levels in hematologic malignancies and has thus become an attractive target of therapy. While CD123 expression in precursor B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) has been reported, only limited data in T-ALL exists. Furthermore, the potential of CD123-targeted therapies in ALL remains largely unexplored. In this study, we examine CD123 expression levels in a large cohort of ALL patients and assess the impact of IMGN632, a conjugate of a CD123-binding antibody with the novel DNA-alkylating IGN payload DGN549, on in vitro viability of patient ALL cells and cell lines.
Methods: The study cohort (n=188) included 162 B-ALL and 26 T-ALL patients diagnosed and treated at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center between 12/2012 and 1/2017. Among B-ALL patients, 59 (36%) were Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+). T-ALL patients were further subtyped into the following immunophenotypic categories: early, early T precursor (ETP), thymic, and mature. CD123 expression was evaluated using multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC). Blasts were defined by lineage markers as well as CD45dim blast gate, and CD123 expression was measured for the percentage of positivity and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ratio over controls. An arbitrary cutoff of 20% was used for expressing nominal MFC results. Median follow up duration was 21.1 months. CD123 expression was correlated with clinical, laboratory, and outcomes results. The number of binding sites for IMGN632 on ALL blast and cell lines was quantified by QuantiBRITE method. Cytotoxicity of IMGN632 was evaluated after continuous exposure up to five days by WST-8 assays on cell lines or by MFC on primary ALL patient samples.
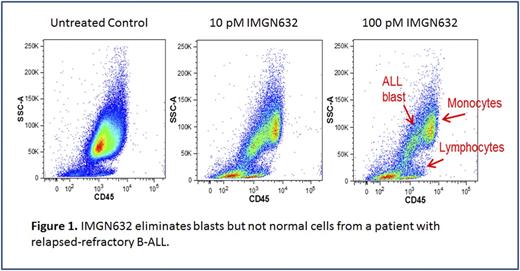
Results: Patients had a median age of 46 years (range, 16-88 years) and included 117 (62%) men. The median CD123 positivity on ALL blasts was 78% (range, 0.3-100) with a median MFI ratio of 11 (range, 0-203). For categorical analysis purposes, we used a standard cutoff of 20% to define positive CD123 expression. Prevalence of CD123 expression was overall higher in B-ALL compared to T-ALL [145 (90%) vs. 11 (42%); p<0.001]. Expression prevalence was highest in Ph+ B-ALL (57/59; 97%) followed by Ph- B-ALL (88/103; 85%) and T-ALL (11/26; 42%). In Ph- B-ALL, CD123 expression correlated with CD34 expression (p=0.002) and lower bone marrow blast count (p=0.003). In T-ALL, CD123 expression correlated with immunophenotypic subtypes (early) (p=0.006). To test the potential of targeting CD123 in ALL, B-ALL cell lines (n=12) which express CD123 at levels similar to AML patient samples were exposed to titrated IMGN632 levels. IMGN632 IC50 values ranged between 0.6 and 20 pM, and the conjugate cytotoxicity was highly CD123-specific, as masking CD123 with a competing anti-CD123 antibody reduced the potency more than 1000-fold. To test the anti-leukemia activity of IMGN632 on primary B-ALL cells, bone marrow cells from B-ALL patients were exposed to IMGN632 following which blasts and non-malignant cells were enumerated by MFC. Notably, IMGN632 eliminated more than 90% of B-ALL blasts in 6 out of 8 samples from newly-diagnosed as well as relapsed-refractory patients at low pico-molar concentrations. Normal cells were not affected by IMGN632 at 100-fold higher concentrations.
Conclusions: CD123 expression is prevalent across ALL subtypes, including 90% of B-ALL and 42% of T-ALL. CD123 expression was associated with CD34 expression in B-ALL and immunophenotype in T-ALL. The CD123 targeted antibody-drug conjugate IMGN632 demonstrates promising activity and safety in pre-clinical models of B-ALL.
_
Daver: Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Consultancy; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy. Zweidler-McKay: ImmunoGen: Employment. Kantarjian: ARIAD: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Khoury: Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding; Kiromics: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Angle: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal